How to do Futures Trading on Phemex
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the fundamentals of futures trading on Phemex, covering key concepts, essential terminology, and step-by-step instructions to help both beginners and experienced traders navigate this exciting market.


- Promotion Period: No limited time
- Available to: All Traders of XT.com
- Promotions: Receive up to 40% for each trade
What is Phemex Perpetual Contract
The main distinction between a Perpetual Contract and a traditional Futures Contract is that the former is a derivative product that allows you to hold a position for as long as you like, while the latter has an expiration date. Futures contracts are an agreement to buy or sell a commodity at a predetermined price at a specified time in the future. Perpetual contracts also trade near the Index Price because they resemble the margin-based spot market. This gives you the opportunity to increase the deal’s potential outcome, but it also means that you will automatically liquidate your equity and close your position if the price of a commodity declines by an amount equal to your initial margin, or the percentage of the total funds you provided as collateral.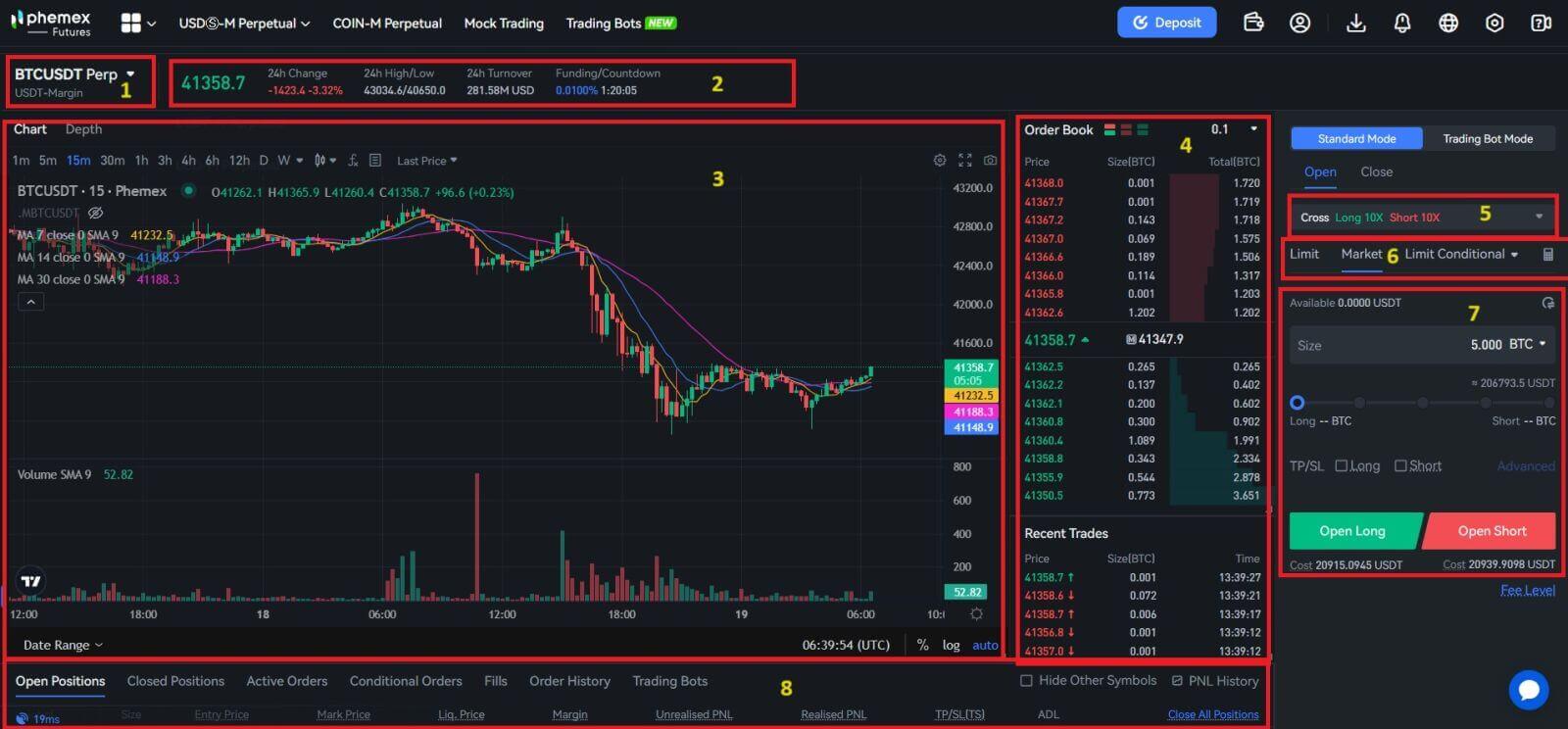
- Trading Pairs: Shows the current contract underlying cryptos. Users can click here to switch to other varieties.
- Trading Data and Funding Rate: Current price, highest price, lowest price, increase/decrease rate, and trading volume information within 24 hours. Display the current and next funding rates.
- TradingView Price Trend: K-line chart of the price change of the current trading pair. On the left side, users can click to select drawing tools and indicators for technical analysis.
- Orderbook and Transaction Data: Display current order book order book and real-time transaction order information.
- Position and Leverage: Switching of position mode and leverage multiplier.
- Order type: Users can choose from a limit order, market order and trigger order.
- Operation panel: Allow users to make fund transfers and place orders.
- Position and Order information: Current position, current orders, historical orders and transaction history.
How to add Funds to Futures account on Phemex
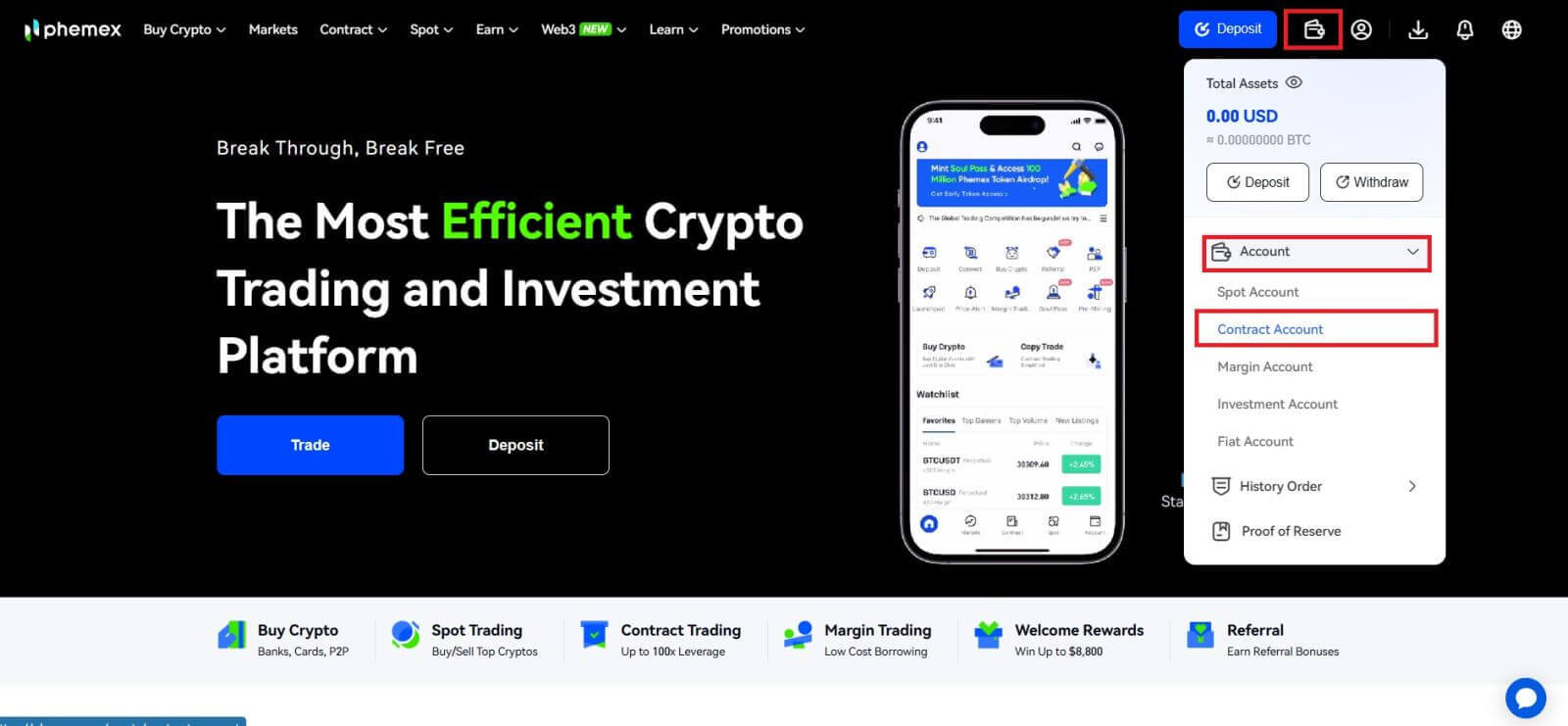
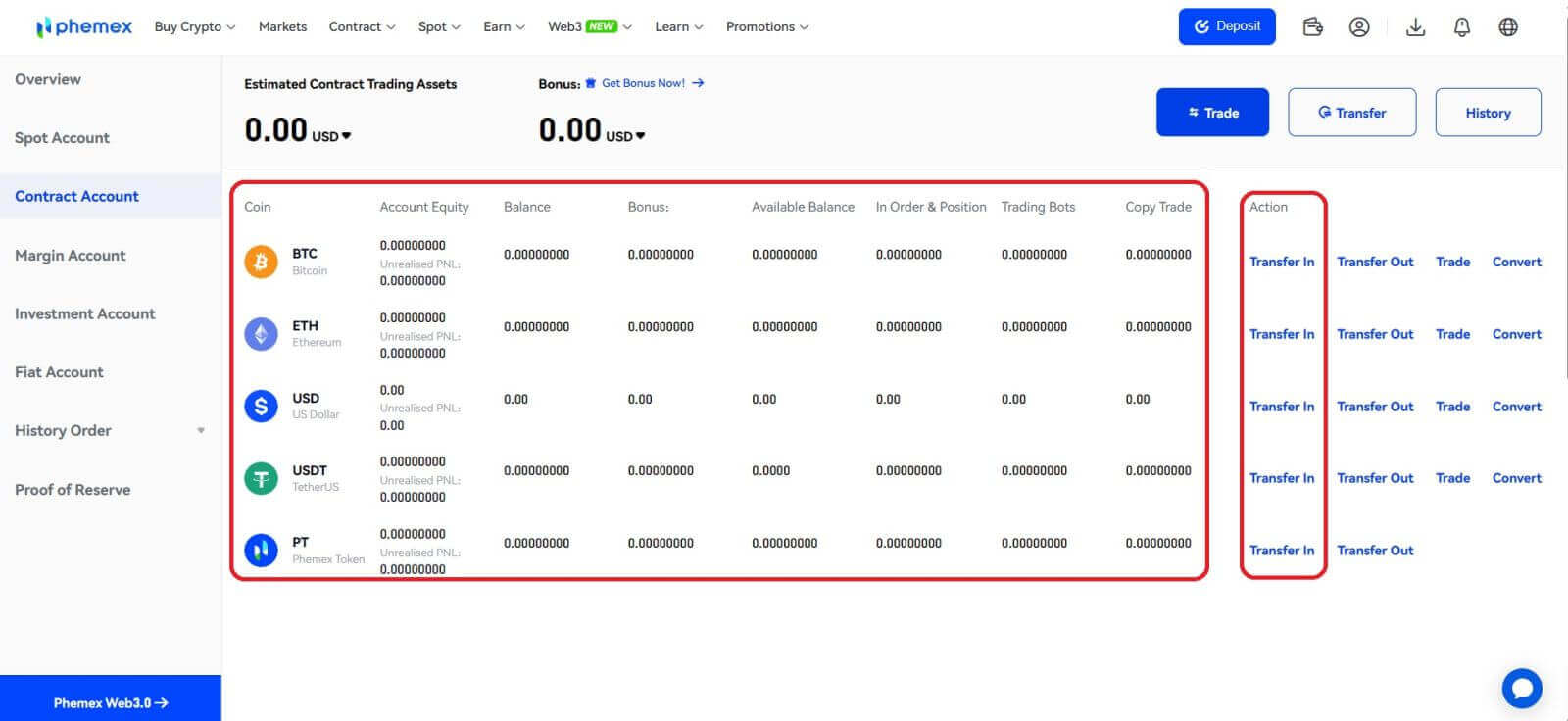
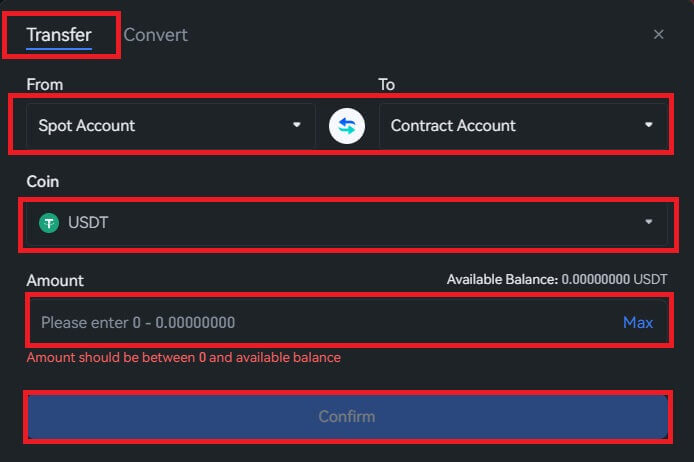
You must fund your futures account before you can begin trading futures. This separate fund influences your trade margins and establishes your risk tolerance. Don’t forget to only transfer money you can afford to lose. The financial security of you or your family should not be jeopardized by futures trading, as it carries greater risk than ordinary cryptocurrency trading.You can move USDT between your current and futures accounts. At the homepage, choose [Total Assets]-[Account]-[Contract Account]. Then you can Transfer In.
How to Trade USDT-M Perpetual Futures on Phemex (Web)
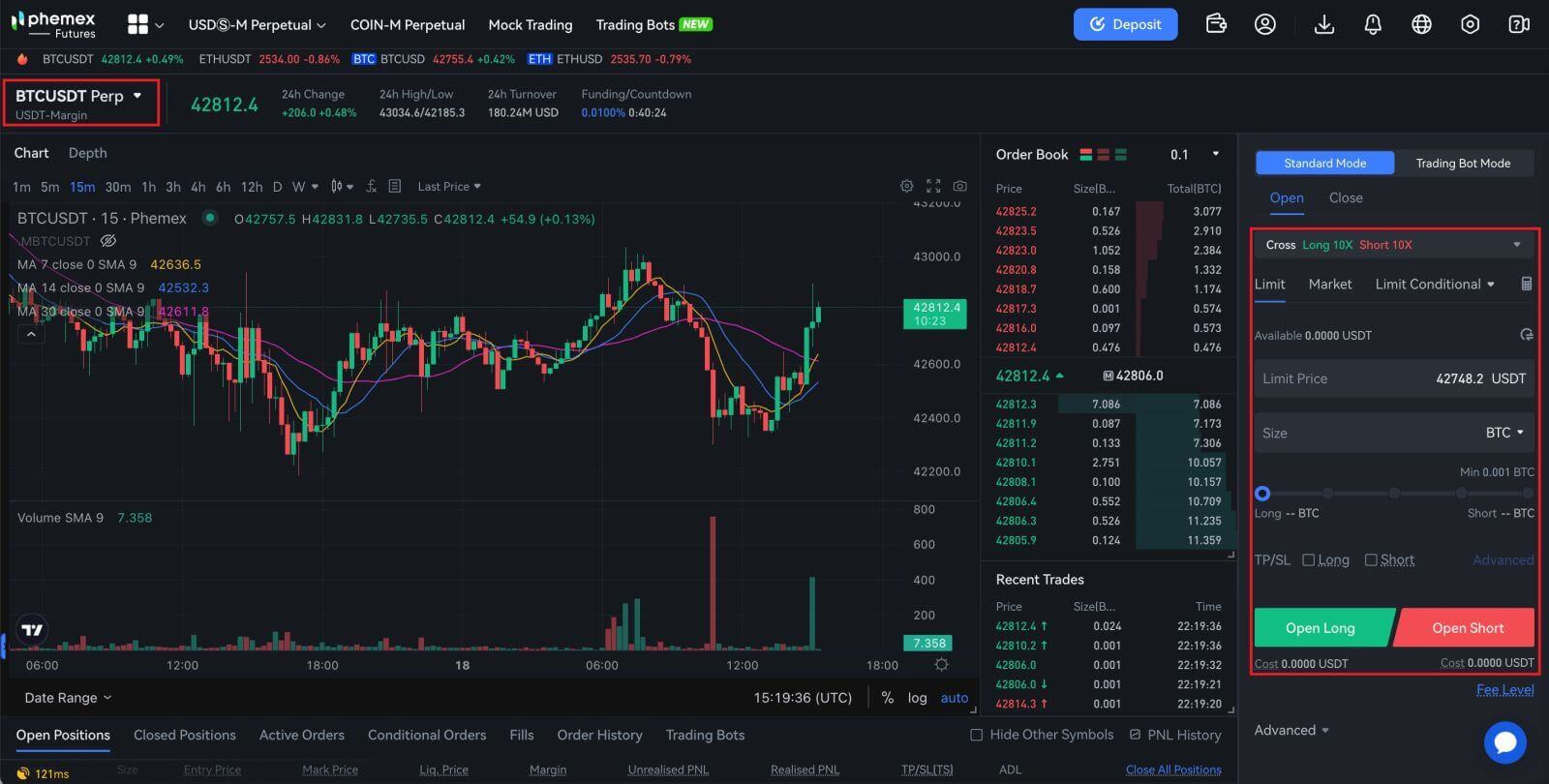
1. Sign in to the Phemex website, then click the tab at the top of the page to go to the "Contract" section.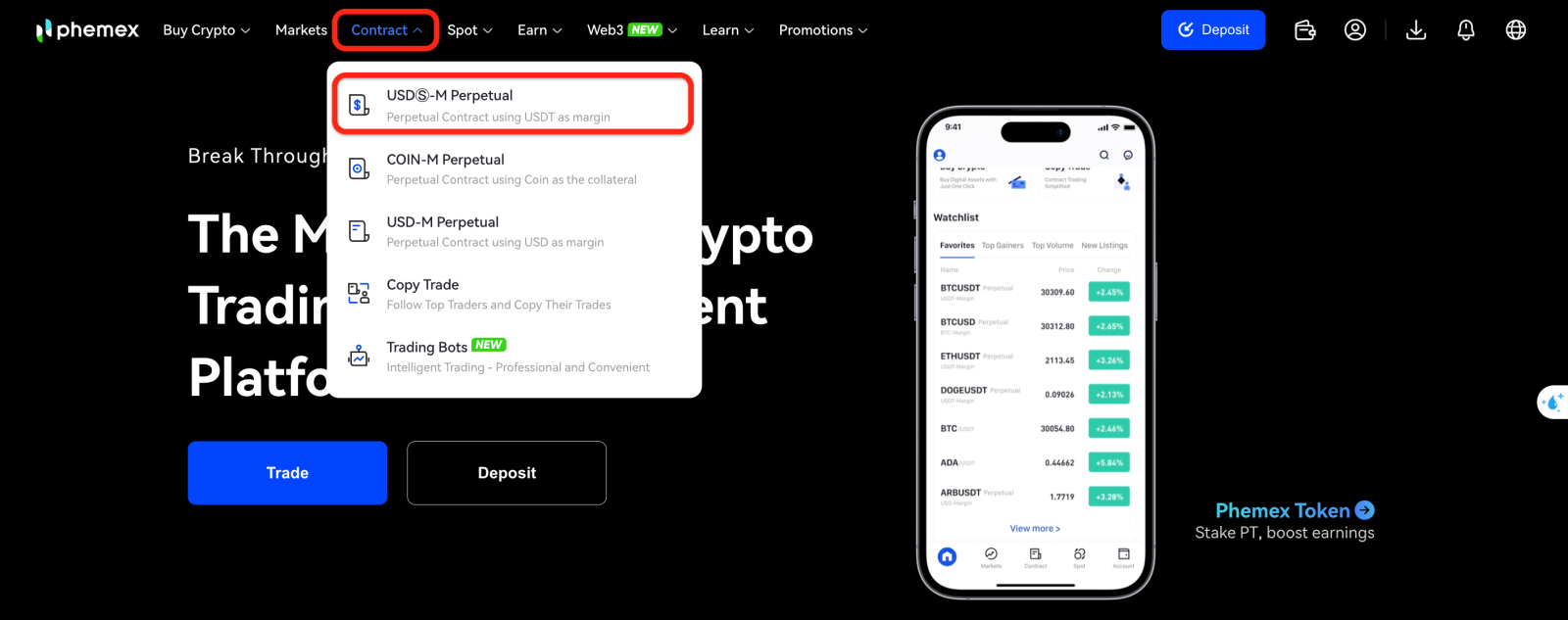
2. From the list of futures on the left, choose BTCUSDT Perp.
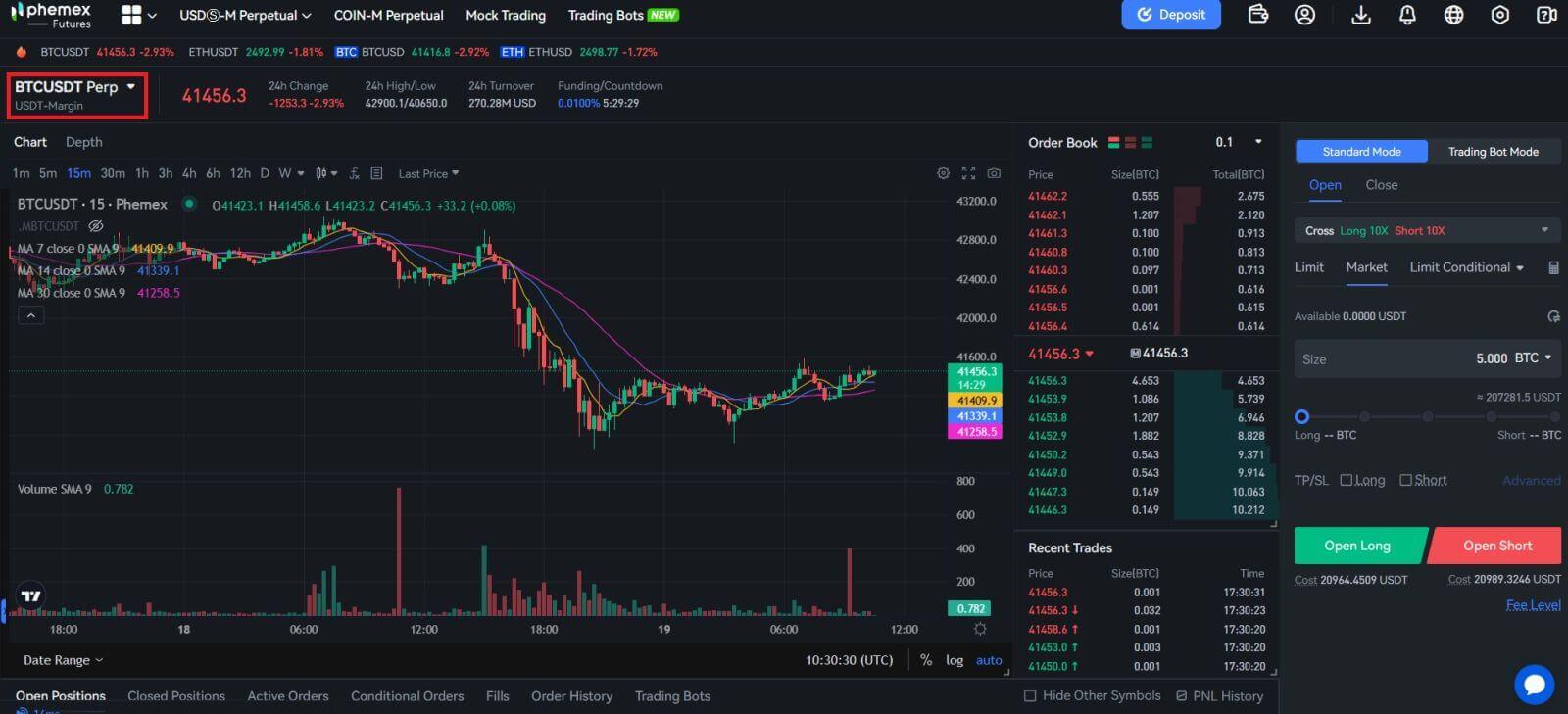
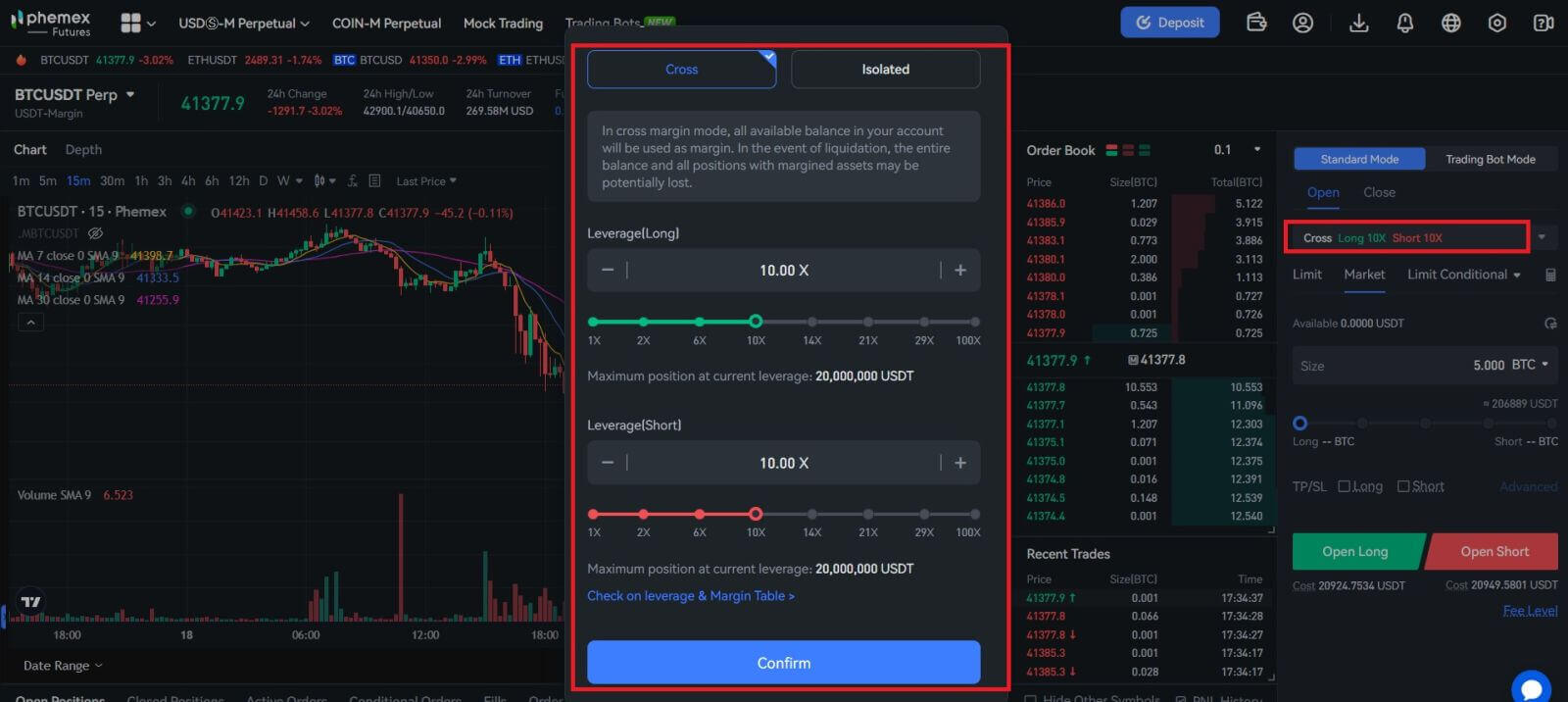
3. To change position modes, select "Position by Position" on the right. Click the number to change the leverage multiplier. For further information, please refer to the specific product details as each product supports a different range of leverage multiples.
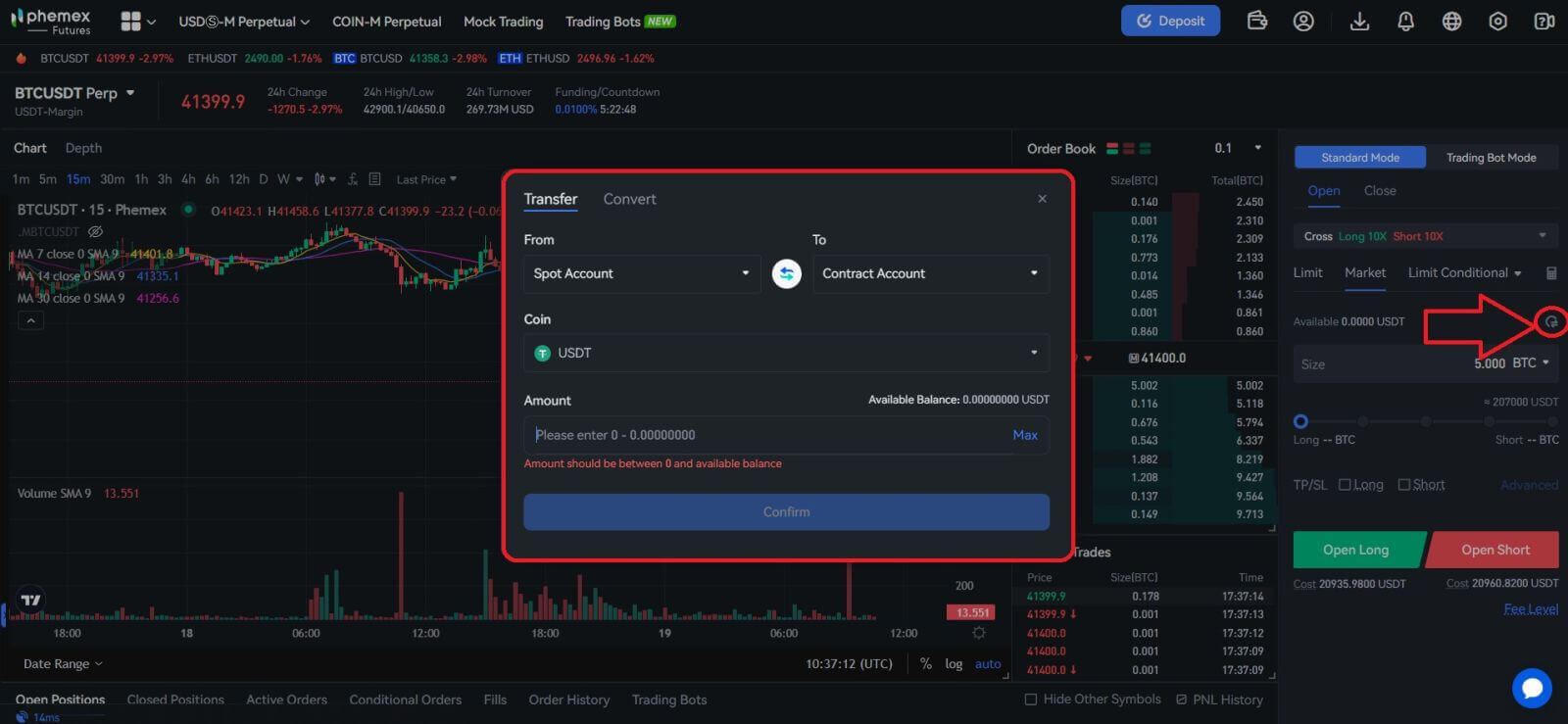
4. To view the transfer menu, click the little arrow button on the right. To move money from the spot account to the futures account, enter the desired amount and hit "Confirm".
5. Users have three options for opening a position: Market Order, Limit Order, and Limit Conditional. After entering the order’s quantity and price, click "Open Long".
- Limit Order: Buyers and sellers determine the price on their own. Only when the market price hits the predetermined price will the order be filled. The limit order will keep waiting for the transaction in the order book if the market price falls short of the predetermined amount;
- Market Order: A market order transaction is one in which neither the purchase price nor the selling price are fixed. The user only needs to enter the order amount; the system will complete the transaction based on the most recent market price at the time of placement.
- Trigger Order: Users must specify the order price, quantity, and trigger price. The order will be placed as a limit order with the previously set price and amount only when the most recent market price reaches the trigger price
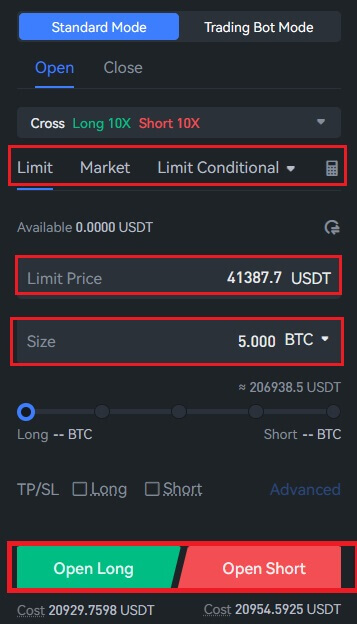
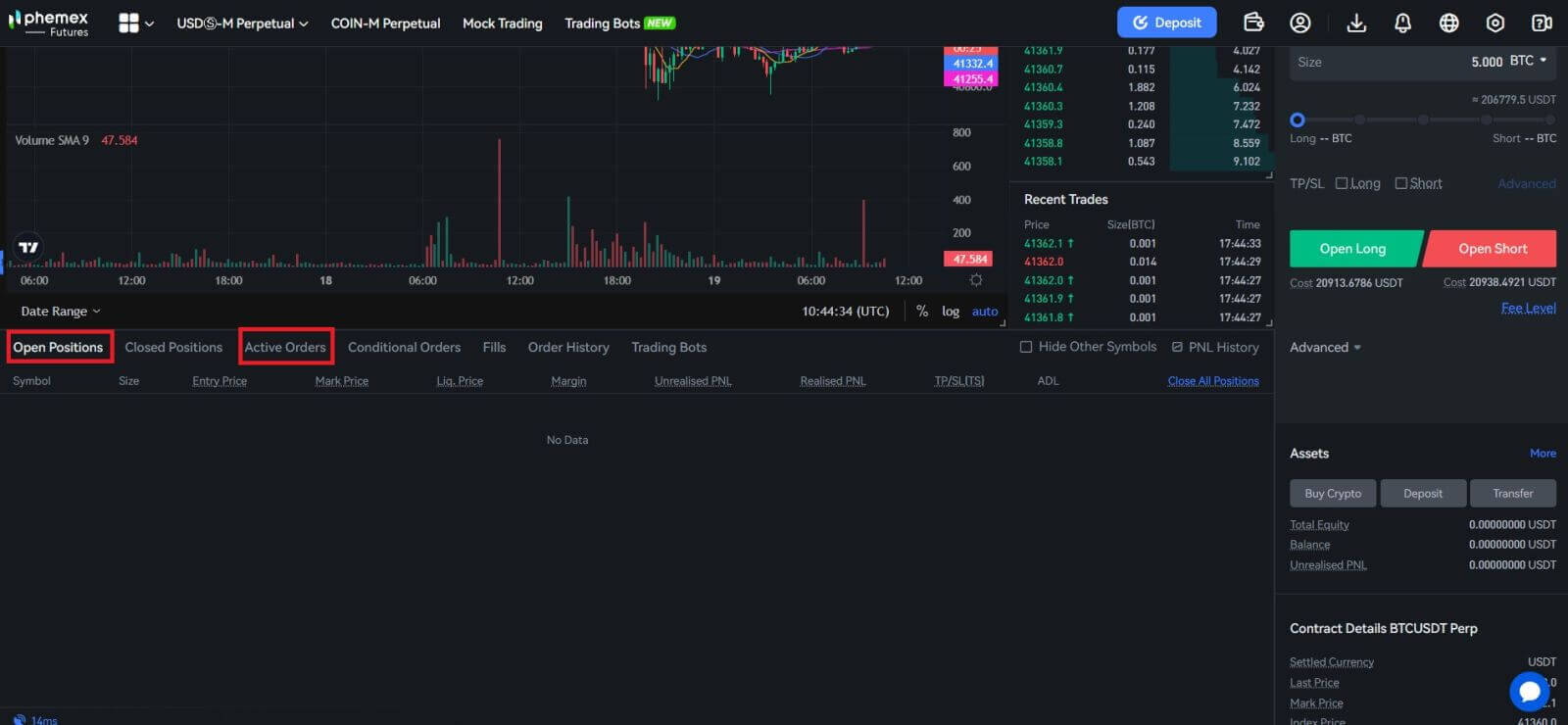
6. View your order by selecting "Active Orders" at the bottom of the page after placing it. Orders can be canceled prior to fulfillment. Upon completion, locate them under "Open Positions".
How to Trade USDT-M Perpetual Futures on Phemex (App)
1. Use the mobile app to log into your Phemex account. Then, navigate to the "Contract" section at the bottom of the screen.
2. To switch between different trading pairs, tap on BTCUSDT, which is located in the upper left corner. To locate the desired futures for trading, use the search bar or choose straight from the options listed.
3. Select the margin mode and change the leverage parameters to suit your needs. Choose Confirm.
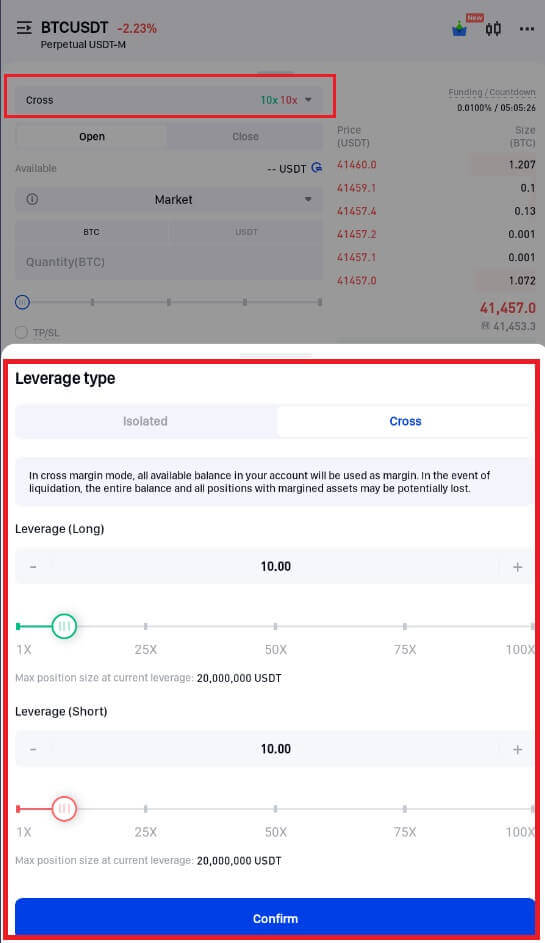
4. Place your order on the screen’s left side. Enter the amount only for a market order and the price and amount for a limit order. Press "Open Long" to start a long position or "Open Short" to start a short position.
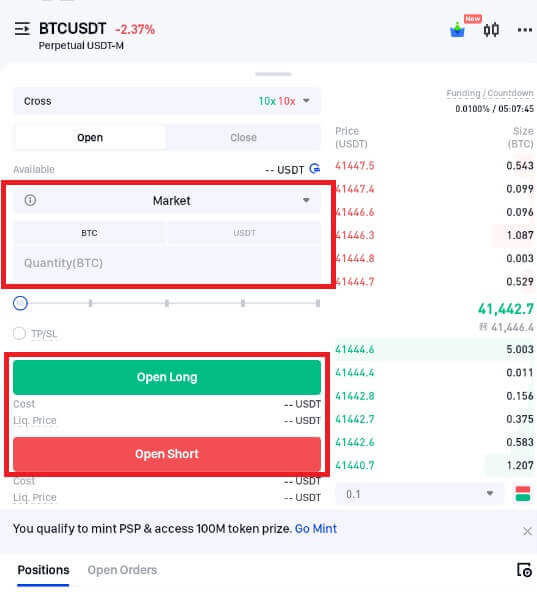
5. If the order is not filled right away after it is placed, it will show up in "Open Orders". It is possible for users to cancel pending orders by tapping "[Cancel]". Orders that have been fulfilled will appear under "Positions".
6. Open "Positions", select "Close", and then input the amount and price needed to close a position.
Futures Trading on Phemex
Margin Mode
Cross and Isolated are the two distinct margin modes that Phemex supports.
- All of the money in your futures account, including any unrealized gains from other open positions, is used as the margin when you use cross margin.
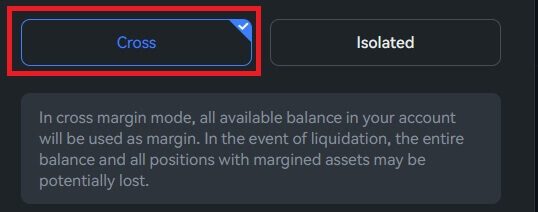
- Conversely, isolated will only use the initial margin amount that you specify.
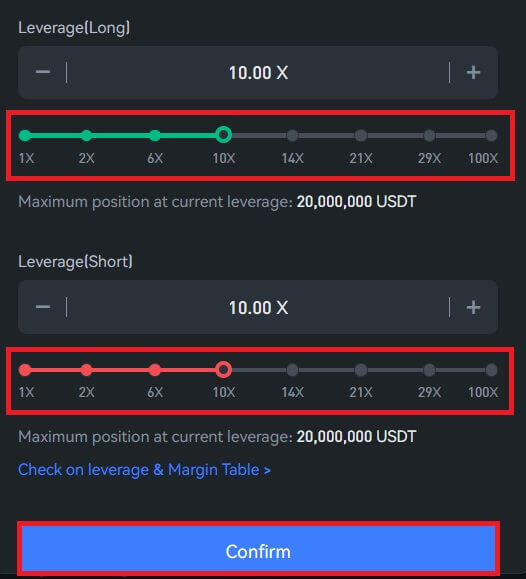
Leverage Multiple (Long/Short)
With a mechanism called leverage, USDT perpetual contracts let you increase the gains and losses on your investments. For instance, you will profit $1 * 3 = $3 if you choose a leverage multiple of 3x and the value of your underlying asset increases by $1. On the other hand, you will lose $3 if the underlying asset drops by $1.The asset you choose to buy and the value of your position will determine the maximum leverage you can use. Larger positions will only be able to access smaller leverage multiples in order to prevent large losses.
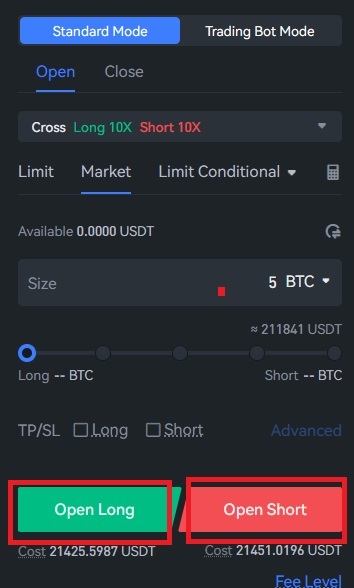
Long or Short
Unlike standard spot trading, perpetual contracts give you the choice to go Open Long (buy) or Open Short (sell).
When you buy long, you are indicating that you think the asset you are purchasing will appreciate in value over time and that you will benefit from this increase, using your leverage to multiply your profit. In contrast, if the asset’s value declines and is once more multiplied by the leverage, you will lose money.
On the other hand, buying short means you think this asset’s value will decrease over time. When the value decreases, you will make money; when the value rises, you will lose money.
There are a few more new ideas you should become acquainted with after opening your position.
How are Crypto Futures Contracts Different From Spot Trading?
Cryptocurrency futures are traded based only on price movement rather than any underlying assets. Since they typically move quickly and settle every day, they are therefore perfect for the cryptocurrency market. Because cryptocurrency assets are very liquid and volatile, or have a lot of movement and profit potential, this works well in the market. High-leverage margin trading is possible with cryptocurrency futures.Additionally, rather than being traded on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like UniSwap or SushiSwap, cryptocurrency futures are traded on more centralized crypto exchanges.
Types of Cryptocurrency Futures Contracts
Contracts for cryptocurrency futures are available in a variety of sizes and forms, each with a special set of advantages and disadvantages.
1) A typical futures agreement
- The most typical kind of contract is a standard futures contract, which is a binding legal agreement to purchase or sell a specific quantity of cryptocurrency at a given price on a future date. Traders can use these contracts, which are standardized to guarantee fairness, to lock in a price for the physical delivery of cryptocurrency, hedge against price risk, and speculate on the future price of cryptocurrencies.
- Standard futures contracts, however, carry the risk of having to deliver the underlying asset or accept its delivery, as well as the potential for futures margin payments or receipts in the event that trader positions are impacted by market movements.
2) Contract delivered in person
- The physically-delivered contract is another kind of cryptocurrency futures contract. These agreements resemble conventional futures agreements, but instead of receiving payment in cash, they settle on the actual delivery of cryptocurrency. When purchasing cryptocurrency for long-term investment purposes, for example, traders who wish to receive physical delivery of the underlying asset frequently use this kind of contract. These contracts do, however, carry some risks, including counterparty and storage risk.
3) Indefinite agreement
- Perpetual contracts represent a category of cryptocurrency futures that lack a predetermined delivery date. Rather, these agreements settle every day and roll over indefinitely. Traders who wish to hedge against volatility risk or speculate on short-term price movements frequently use perpetual contracts.
- However, in the event that prices move sharply against trading positions, these contracts—which lack a fixed expiration date—may be vulnerable to significant mark-to-market swings. Perpetual contracts are therefore regarded as somewhat risky financial instruments and are not appropriate for all investors.
- Major cryptocurrency exchanges, like Phemex, which provides BTC and USD perpetual contracts, have embraced crypto perpetual contracts.
How to Trade Crypto Futures Profitably
- Recognize your exchange. It is crucial to conduct thorough research and choose an exchange that aligns with your requirements, as not all exchanges provide identical goods or services.
- Think about how much risk you can take. Before investing any money, it’s critical to comprehend the risks associated with futures trading as it may not be suitable for all investors.
- Make a plan. It is essential to have a clear plan in place before making any trading decisions. Make an effort to have a clear idea of your entry point into the trade as well as your planned exit strategy.
- Have patience. Impatient beginners to futures trading frequently try to force trades, which is usually a surefire way to end up badly. When trading futures, waiting for the right opportunity and exercising patience are crucial.
- Control your exposure to risk. Risk management is one of the key components of futures trading. Make sure you establish take-profit and stop-loss levels, and avoid overly leveraging your position. Gaining profitable experience in bitcoin futures trading will come easily to you if you can grasp these five concepts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are crypto futures?
Financial contracts known as cryptocurrency futures enable two parties to decide to buy or sell a cryptocurrency at a specific future date and price. Without actually owning the assets, futures can be used to speculate on the price movement of cryptocurrencies or as a risk hedge.Cryptocurrency futures are typically traded on margin, requiring collateral from both parties. Cash, cryptocurrency, or other assets may be used as collateral. Frequently, the collateral’s worth exceeds the contract’s actual value by a large margin.
For instance, $100,000 in collateral may be needed for a $10,000 Bitcoin futures contract. Due to the extreme volatility and quick swings in cryptocurrency prices, this high level of collateral is required. One party to a contract is required to provide additional collateral to cover their positions when they purchase or sell the underlying asset (in this case, Bitcoin). They will lose money if the price moves against them and they are unable to post additional collateral. This is known as liquidation of position.
Insurance products that guard against price fluctuations are available on certain exchanges, but they might not cover all kinds of losses and aren’t always available. Investors need to have an account with a broker that offers these products in order to trade cryptocurrency futures. In addition to a daily charge for positions held overnight, brokers usually charge commission on each trade. If the account is not in USD, some brokers additionally charge for currency conversions.
Exchanges for cryptocurrency futures allow for both spot and margin trading. While margin exchanges enable investors to trade with leverage, spot exchanges let investors buy and sell cryptocurrencies at the current price.
Since leverage increases both gains and losses, it is best to use it sparingly. In general, well-capitalized investors who can tolerate possible losses and are accustomed to volatile markets should consider investing in cryptocurrency futures.
Bitcoin Futures – How Does It Work?
The most well-known kind of cryptocurrency futures contract, bitcoin futures, were first offered by the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) in December 2017. Since then, a number of other exchanges, such as the Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE) and the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), have introduced cryptocurrency futures.
With Bitcoin futures, investors can benefit from price discovery, transparency, and risk management features while still having a safety net in place for any direct exposure. If you want more control over your investment than simply purchasing coins from an exchange or taking risks on sudden fluctuations in cryptocurrency prices, this is ideal.For instance, you could purchase a Bitcoin futures contract if you anticipate that the price of Bitcoin will increase in the future. In the event that Bitcoin’s price increases as predicted, your contract will yield a profit. In the event that the price drops, you would lose money. There are cryptocurrency exchanges that allow trading with futures contracts.
Leverage trading is an option for these contracts, allowing you to control a much larger portion of the underlying asset with a small initial investment. This may increase your profits or losses. Because of this, trading futures requires a higher level of skill and is not appropriate for all traders.

